
Egg-parasitoids wasp of Deielia phaon
The final renewal day of this page is September15, 2003.

Figure3-1: 1. Deielia phaonCoviposition.@Deielia phaon is Libellulidae. Deielia phaon lays eggs in the stems or leaves of the plant on the surface of the water. 2. The inhabiting environment of Deielia phaon Deielia phaon likes the shallow pond where a read and a read-mace grow. And, it inhabits the river where flow is slow, too.

Figure3-2:Eggs of Deielia phaon @@@Many eggs stick to the surface of the plant.

@
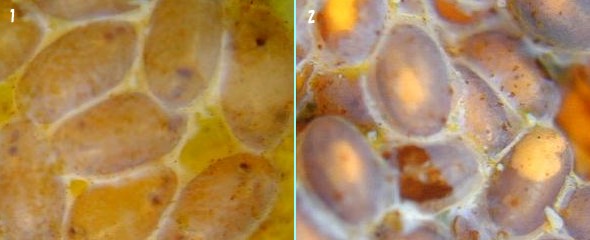
Figure3-3: 1. Some eggs of Deielia phaon@2. Some eggs of Deielia phaon that egg-parasitoid parasitized it.
The larva of this egg-parasitoids wasp becomes a pupa in the egg, and emergences. The period until it emergences is longer than the egg duration of Deielia phaon. The egg which doesn't hatch easily blackish is the egg which egg-parasitoids wasp parasitizes. It can be distinguished because it is yellow just before the emergence.
@
Figure3-4: 1. The egg-parasitoid emale of Deielia phaon@2. An egg-parasitoid just before the emergence
The egg of Deielia phaon is small in comparison with Aeshnidae and Lestidae. Therefore, egg-parasitoids wasp is small,too. Size: ;body length 0.55mm.

@
Figure3-5: 1. (under water) 2. ; It is laying eggs in the egg of Deielia phaon. (under water)
As for the male, the color of the first half part of the body has yellow. The body of the female is blackish, and the tip of the abdomen of it isn't round like a male, and a little sharp. The male which went from the egg is walking the neighborhood with the egg of Deielia phaon. A male helps a female go from the egg in the time. A male copulates soon when a female goes from the egg. Copulation time is several seconds. A female lays eggs in the egg of Deielia phaon soon after the copulation.

@